Overview
Table format
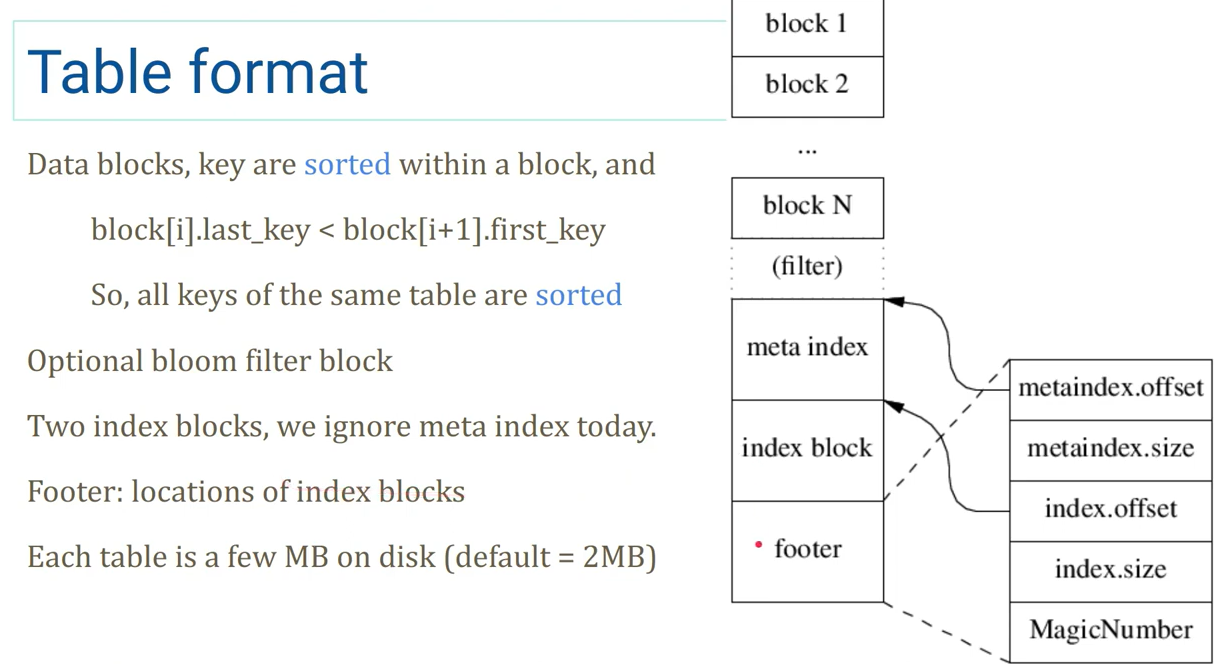
-
倒着读,顺序写
-
中间包含一个
filter,默认是BloomFilter -
footer中的 offset 和 size 使用的是变长数,即支持理论上无限大的存储器(然而事实上不会超过uint64能表示的范围)- 目前长度有上限,四个数总共不能超过
2*BlockHandle::kMaxEncodedLength == 40B,也就是每个数可以比uint64多两个 bytes - 使用变长大概是为了兼容考虑,如果哪天 40B 也不够用了拓展后依然能读旧的 table
- 目前长度有上限,四个数总共不能超过
-
footer有 padding,确保长度是 40B(除去 8B 的 magic number)
Data block(Block)
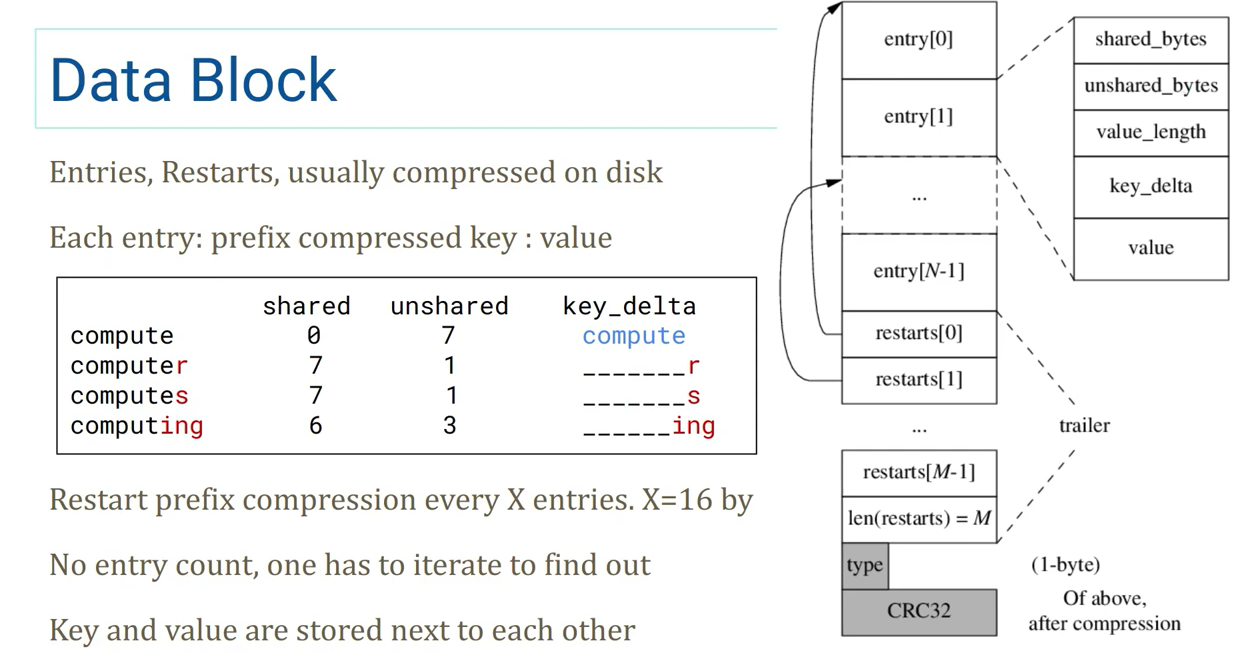
-
倒着读,算出 entries 的长度
-
type 和 CRC32 只在硬盘里,entries 和 restarts 在磁盘上存储时会压缩(no mmap)
-
restarts 是有序的,所以可以当作这个 Data Block 的一层索引
-
entry 的 key 有前缀压缩,restart 会重置前缀压缩的起始点,默认X=16个重置一次
- X 取一页可以放下的 entries 应该是最好的,这样往前读 restart 可以命中同一个 page,不会增加磁盘IO
Index block
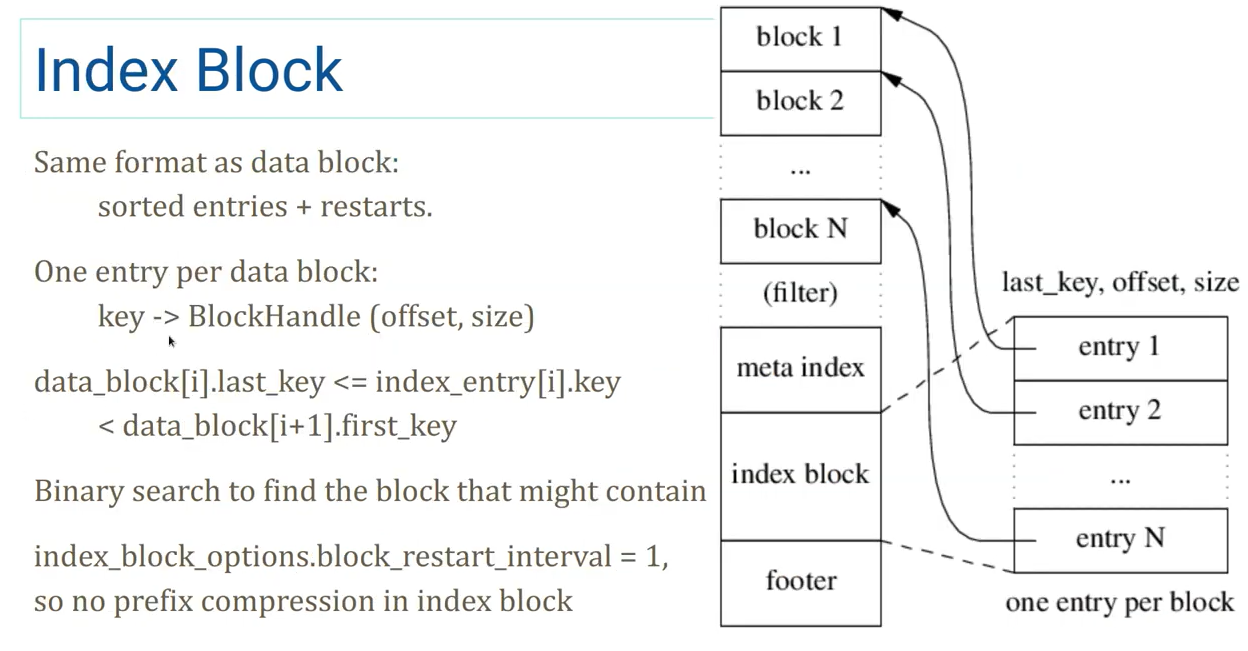
-
为全部 Data Block 建立的一层索引
-
结构和 Data Block 完全一样,只不过 value 是
BlockHandle(offset, size),指向一个 Data Block -
也有 restarts(图中没画出),同样这个 restarts 也可以作为这个 Index Block 的一层索引
- 检索流程 Index block restarts -> Index block -> Data block restarts -> Data block
-
Index Block 的 key(last_key) 是它所指向的 Data Block 到下一个 Data Block 之间的 key,这样可以压缩 Index Block 的 last_key
- 如果
DataBlock[3].last_key = "abcdefghi",DataBlock[4].first_key= "c" - 那么
IndexBlock[3].last_key可以是"b",如果大于"b",那就说明不在这个DataBlock里,这样就可以不用存"abcdefghi",只用存"b"了
- 如果
Meta block
- 自定义的 Block 结构,目前内置的只有一个 meta block 可用:filter block
- 默认是布隆过滤器
Filter block 结构:

- 每一个
filter[i]表示从[i*base, (i+1)*base-1]的 key 使用FilterPolicy::CreateFilter()创建出来的 filterbase目前是2KB
- 下面的 offset 可以让 data block offset 快速 map 到对应的 filter 上
- 最后 5 个 bytes 的 trailer
- 4B 指向 offset 的开始
- 1B 表示
log(base)
Meta index block
- 类似 index block,key 是 meta block 的名称,value 也是
BlockHandle(offset, size)
Log format
- 固定的 block 大小
- 32KB
- 每个 block 里有多个 record
- 每个 record 前 7 个字节为 header,4 个 crc32,2 个 length,1 个 type
- 后面是 char[length] 的数据
- 三种 type
- Zero:mmap 时会使用这个类型,读到会返回 BadRecord
- Full:完整的一个记录
- Fisrt/Middle/Last:分片记录,它们会合并到一起当作一个 record 提供给外部
到这基本上就已经知道 reader 是如何实现的了,接下来是具体的实现的代码解析,可以从中学到一些工程设计。
Implementation
Reader
Dump File 的实现会把所有的 Reader 整合在一起,跟着执行路径读应该能看完大部分的 Reader 实现
解析后的格式:
// XXXXXX.log
--- offset 0; sequence 257
put 'Key0' 'Test data value: 0'
--- offset 44; sequence 258
put 'Key1' 'Test data value: 1'
...
// XXXXXX.ldb:
'Key0' @ 1 : val => 'Test data value: 0'
'Key1' @ 2 : val => 'Test data value: 1'
'Key10' @ 11 : val => 'Test data value: 10'
'Key100' @ 101 : val => 'Test data value: 100'
'Key101' @ 102 : val => 'Test data value: 101'
'Key102' @ 103 : val => 'Test data value: 102'
...
// MANIFEST-XXXXXX:
--- offset 0; VersionEdit {
Comparator: leveldb.BytewiseComparator
}
--- offset 35; VersionEdit {
LogNumber: 6
PrevLogNumber: 0
NextFile: 7
LastSeq: 256
AddFile: 0 5 2396 'Key0' @ 1 : 1 .. 'Key99' @ 100 : 1
}
实现:
// 文件类型
enum FileType {
kLogFile, // XXXXXX.log
kDBLockFile, // LOCK
kTableFile, // XXXXXX.sst/.ldb
kDescriptorFile, // MANIFEST-XXXXXX
kCurrentFile, // CURRENT
kTempFile, // XXXXXX.dbtmp
kInfoLogFile // LOG/LOG.old
};
Status DumpFile(Env* env, const std::string& fname, WritableFile* dst) {
FileType ftype;
if (!GuessType(fname, &ftype)) {
return Status::InvalidArgument(fname + ": unknown file type");
}
// 根据文件类型分别解析
switch (ftype) {
case kLogFile:
return DumpLog(env, fname, dst);
case kDescriptorFile:
return DumpDescriptor(env, fname, dst);
case kTableFile:
return DumpTable(env, fname, dst);
default:
break;
}
return Status::InvalidArgument(fname + ": not a dump-able file type");
}
DumpLog/DumpDescriptor
Status DumpLog(Env* env, const std::string& fname, WritableFile* dst) {
return PrintLogContents(env, fname, WriteBatchPrinter, dst);
}
// Called on every log record (each one of which is a WriteBatch)
// found in a kLogFile.
// 最终输出到文件的函数,一些字符串拼接操作
static void WriteBatchPrinter(uint64_t pos, Slice record, WritableFile* dst) {
std::string r = "--- offset ";
AppendNumberTo(&r, pos);
r += "; ";
if (record.size() < 12) {
r += "log record length ";
AppendNumberTo(&r, record.size());
r += " is too small\n";
dst->Append(r);
return;
}
// 把读出来的 record 丢到 WriteBatch,相当于 WriteBatch 的 content 就是落盘时的数据了
// 然后迭代 WriteBatch,传入一个自定义的 Handle(把迭代的内容写到 dst 里),就可以解析了
WriteBatch batch;
// 设置 Writer buffer
WriteBatchInternal::SetContents(&batch, record);
r += "sequence ";
AppendNumberTo(&r, WriteBatchInternal::Sequence(&batch));
r.push_back('\n');
dst->Append(r);
// 自定义的 Handle,把迭代的内容写到 dst 里
WriteBatchItemPrinter batch_item_printer;
batch_item_printer.dst_ = dst;
Status s = batch.Iterate(&batch_item_printer);
if (!s.ok()) {
dst->Append(" error: " + s.ToString() + "\n");
}
}
// Print contents of a log file. (*func)() is called on every record.
Status PrintLogContents(Env* env, const std::string& fname,
void (*func)(uint64_t, Slice, WritableFile*),
WritableFile* dst) {
SequentialFile* file;
Status s = env->NewSequentialFile(fname, &file);
if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
// 遇到 Corruption 会贴到输出文件里
CorruptionReporter reporter;
reporter.dst_ = dst;
// 主要使用 log::Reader 读,启用了 checksum,从 0 开始读
log::Reader reader(file, &reporter, true, 0);
Slice record;
std::string scratch; // 这只当作一个 StringBuffer 用,ReadRecord 不应该每次调用都分配一次内存(可以用个全局变量啊?)
while (reader.ReadRecord(&record, &scratch)) {
(*func)(reader.LastRecordOffset(), record, dst);
}
delete file;
return Status::OK();
}
// Called on every log record (each one of which is a WriteBatch)
// found in a kDescriptorFile.
static void VersionEditPrinter(uint64_t pos, Slice record, WritableFile* dst) {
std::string r = "--- offset ";
AppendNumberTo(&r, pos);
r += "; ";
VersionEdit edit;
// 解析 VersionEdit,里面按序存了一些 metadata
Status s = edit.DecodeFrom(record);
if (!s.ok()) {
r += s.ToString();
r.push_back('\n');
} else {
r += edit.DebugString();
}
dst->Append(r);
}
Status DumpDescriptor(Env* env, const std::string& fname, WritableFile* dst) {
return PrintLogContents(env, fname, VersionEditPrinter, dst);
}
Log
定义
class Reader {
public:
// Interface for reporting errors.
// 遇到 Corruption 时的处理,读坏了提供一些信息
class Reporter {
public:
virtual ~Reporter();
// Some corruption was detected. "bytes" is the approximate number
// of bytes dropped due to the corruption.
virtual void Corruption(size_t bytes, const Status& status) = 0;
};
// Create a reader that will return log records from "*file".
// "*file" must remain live while this Reader is in use.
//
// If "reporter" is non-null, it is notified whenever some data is
// dropped due to a detected corruption. "*reporter" must remain
// live while this Reader is in use.
//
// If "checksum" is true, verify checksums if available.
//
// The Reader will start reading at the first record located at physical
// position >= initial_offset within the file.
Reader(SequentialFile* file, Reporter* reporter, bool checksum,
uint64_t initial_offset);
// 只允许引用传递
Reader(const Reader&) = delete;
Reader& operator=(const Reader&) = delete;
~Reader();
// Read the next record into *record. Returns true if read
// successfully, false if we hit end of the input. May use
// "*scratch" as temporary storage. The contents filled in *record
// will only be valid until the next mutating operation on this
// reader or the next mutation to *scratch.
// 主要的方法,读一个记录放到 record 里,第二个参数 scratch 用来拼接分片的记录(为什么不用成员变量?)
bool ReadRecord(Slice* record, std::string* scratch);
// Returns the physical offset of the last record returned by ReadRecord.
//
// Undefined before the first call to ReadRecord.
// 上一次读的记录的物理 offset,如果是分片的记录,返回分片第一个记录的物理 offset
uint64_t LastRecordOffset();
private:
// Extend record types with the following special values
enum {
kEof = kMaxRecordType + 1,
// Returned whenever we find an invalid physical record.
// Currently there are three situations in which this happens:
// * The record has an invalid CRC (ReadPhysicalRecord reports a drop)
// * The record is a 0-length record (No drop is reported)
// * The record is below constructor's initial_offset (No drop is reported)
kBadRecord = kMaxRecordType + 2
};
// Skips all blocks that are completely before "initial_offset_".
//
// Returns true on success. Handles reporting.
bool SkipToInitialBlock();
// Return type, or one of the preceding special values
unsigned int ReadPhysicalRecord(Slice* result);
// Reports dropped bytes to the reporter.
// buffer_ must be updated to remove the dropped bytes prior to invocation.
void ReportCorruption(uint64_t bytes, const char* reason);
void ReportDrop(uint64_t bytes, const Status& reason);
SequentialFile* const file_;
Reporter* const reporter_;
bool const checksum_;
// store 大小是固定的 kBlockSize,所以不需要扩容,指针地址也不会改变
char* const backing_store_;
Slice buffer_;
bool eof_; // Last Read() indicated EOF by returning < kBlockSize
// Offset of the last record returned by ReadRecord.
uint64_t last_record_offset_;
// Offset of the first location past the end of buffer_.
uint64_t end_of_buffer_offset_;
// Offset at which to start looking for the first record to return
uint64_t const initial_offset_;
// True if we are resynchronizing after a seek (initial_offset_ > 0). In
// particular, a run of kMiddleType and kLastType records can be silently
// skipped in this mode
bool resyncing_;
};
实现
enum RecordType {
// Zero is reserved for preallocated files
kZeroType = 0,
kFullType = 1,
// For fragments
kFirstType = 2,
kMiddleType = 3,
kLastType = 4
};
static const int kMaxRecordType = kLastType;
// int16 最大值,大小是固定的,并非 DataBlock 一样可以运行时改变
static const int kBlockSize = 32768;
// Header is checksum (4 bytes), length (2 bytes), type (1 byte).
static const int kHeaderSize = 4 + 2 + 1;
Reader::Reader(SequentialFile* file, Reporter* reporter, bool checksum,
uint64_t initial_offset)
: file_(file),
reporter_(reporter),
checksum_(checksum),
backing_store_(new char[kBlockSize]),
buffer_(),
eof_(false),
last_record_offset_(0),
end_of_buffer_offset_(0),
initial_offset_(initial_offset),
resyncing_(initial_offset > 0) {}
Reader::~Reader() { delete[] backing_store_; }
// 跳到 initial_offset 所指向的 block
bool Reader::SkipToInitialBlock() {
const size_t offset_in_block = initial_offset_ % kBlockSize;
// 当前 offset 所在的 block 的首个字节位置
uint64_t block_start_location = initial_offset_ - offset_in_block;
// Don't search a block if we'd be in the trailer
// trailer 会占用一个 block 最后 6 个字节
if (offset_in_block > kBlockSize - 6) {
// 如果当前 offset 在 trailer 里,就跳过这个 block
block_start_location += kBlockSize;
}
// 记录一下当前读的点
end_of_buffer_offset_ = block_start_location;
// Skip to start of first block that can contain the initial record
if (block_start_location > 0) {
// seek file cursor
Status skip_status = file_->Skip(block_start_location);
if (!skip_status.ok()) {
ReportDrop(block_start_location, skip_status);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool Reader::ReadRecord(Slice* record, std::string* scratch) {
// 确保第一次读之前先 seek 到 initial_offset_
if (last_record_offset_ < initial_offset_) {
if (!SkipToInitialBlock()) {
return false;
}
}
scratch->clear();
record->clear();
// 是不是正在解读分片记录
bool in_fragmented_record = false;
// Record offset of the logical record that we're reading
// 0 is a dummy value to make compilers happy
uint64_t prospective_record_offset = 0;
Slice fragment;
while (true) {
const unsigned int record_type = ReadPhysicalRecord(&fragment);
// ReadPhysicalRecord may have only had an empty trailer remaining in its
// internal buffer. Calculate the offset of the next physical record now
// that it has returned, properly accounting for its header size.
// 当前读到的 block 的物理 offset
uint64_t physical_record_offset =
end_of_buffer_offset_ - buffer_.size() - kHeaderSize - fragment.size();
if (resyncing_) {
// 如果 seek 到的 initial_offset_ 是分片记录,并且是中间或者末尾的记录,那么跳过这些记录,从第一个完整的记录开始
if (record_type == kMiddleType) {
continue;
} else if (record_type == kLastType) {
resyncing_ = false;
continue;
} else {
resyncing_ = false;
}
}
switch (record_type) {
case kFullType:
if (in_fragmented_record) {
// 分片的记录中间不该出现一个 fulltype 记录
// Handle bug in earlier versions of log::Writer where
// it could emit an empty kFirstType record at the tail end
// of a block followed by a kFullType or kFirstType record
// at the beginning of the next block.
if (!scratch->empty()) {
ReportCorruption(scratch->size(), "partial record without end(1)");
}
}
prospective_record_offset = physical_record_offset;
scratch->clear();
*record = fragment;
last_record_offset_ = prospective_record_offset;
return true; // 读到了一个完整的
case kFirstType:
if (in_fragmented_record) {
// 同上,分片还没结束不应该又出现一个分片开头
// Handle bug in earlier versions of log::Writer where
// it could emit an empty kFirstType record at the tail end
// of a block followed by a kFullType or kFirstType record
// at the beginning of the next block.
if (!scratch->empty()) {
ReportCorruption(scratch->size(), "partial record without end(2)");
}
}
// prospective_record_offset 在读分片记录时会一直指向分片开始的 block 的开头的物理 offset,而不是上一次读取到的 block 的开头的物理 offset
prospective_record_offset = physical_record_offset;
scratch->assign(fragment.data(), fragment.size()); // 重置分片的 scratch
in_fragmented_record = true; // 开始读分片记录了
break;
case kMiddleType:
if (!in_fragmented_record) {
// middle 记录需要在 first 之后
ReportCorruption(fragment.size(),
"missing start of fragmented record(1)");
} else {
scratch->append(fragment.data(), fragment.size()); // 贴到 scratch 后面
}
break;
case kLastType:
if (!in_fragmented_record) {
ReportCorruption(fragment.size(),
"missing start of fragmented record(2)");
} else {
scratch->append(fragment.data(), fragment.size());
*record = Slice(*scratch);
// 正确地读完一整块分片,记录一下 last_record_offset_ 为分片开头的 block 的物理 offset
last_record_offset_ = prospective_record_offset;
// 这里是不是忘了 in_fragmented_record = false ?
return true; // 读到了一个完整的
}
break;
case kEof:
if (in_fragmented_record) {
// This can be caused by the writer dying immediately after
// writing a physical record but before completing the next; don't
// treat it as a corruption, just ignore the entire logical record.
// writer 写分片记录写一半挂了,reader 只能读出一半来,把之前填充的 scratch 清理掉
scratch->clear();
}
return false;
case kBadRecord:
if (in_fragmented_record) {
ReportCorruption(scratch->size(), "error in middle of record");
in_fragmented_record = false;
scratch->clear();
}
break;
default: {
// 读到了不认得的 block type
char buf[40];
std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "unknown record type %u", record_type);
ReportCorruption(
(fragment.size() + (in_fragmented_record ? scratch->size() : 0)),
buf);
in_fragmented_record = false;
scratch->clear();
break;
}
}
}
return false;
}
uint64_t Reader::LastRecordOffset() { return last_record_offset_; }
void Reader::ReportCorruption(uint64_t bytes, const char* reason) {
ReportDrop(bytes, Status::Corruption(reason));
}
void Reader::ReportDrop(uint64_t bytes, const Status& reason) {
if (reporter_ != nullptr &&
end_of_buffer_offset_ - buffer_.size() - bytes >= initial_offset_) {
reporter_->Corruption(static_cast<size_t>(bytes), reason);
}
}
unsigned int Reader::ReadPhysicalRecord(Slice* result) {
while (true) {
if (buffer_.size() < kHeaderSize) { // 如果当前读到的 buffer 里没有数据(内容比 header size 还小)
if (!eof_) {
// Last read was a full read, so this is a trailer to skip
buffer_.clear();
// 读一个 block,buffer 重置为指向 backing_store_ 的一个切片
Status status = file_->Read(kBlockSize, &buffer_, backing_store_);
end_of_buffer_offset_ += buffer_.size(); // 一直往后读,不会跳过,所以只需要加大小就是 end offset
if (!status.ok()) { // 读坏了!
buffer_.clear();
ReportDrop(kBlockSize, status);
eof_ = true;
return kEof;
} else if (buffer_.size() < kBlockSize) { // 读完发现没读完整一个 Block,说明已经结束了
eof_ = true;
}
// 我还能读!
continue;
} else {
// Note that if buffer_ is non-empty, we have a truncated header at the
// end of the file, which can be caused by the writer crashing in the
// middle of writing the header. Instead of considering this an error,
// just report EOF.
// writer 写 header 写一半挂了,reader 读到最后一个 block 发现只有半个 header,就会走到
// 这里。buffer 这时可能还有东西(半个 header),清理掉然后当作 EOF 处理
buffer_.clear();
return kEof;
}
}
// buffer 里现在有一个 record 的数据了,开始解析
// Parse the header
// 前 4 个 Bytes 是 crc32
// 第 5,6 两个字节表示长度,第6个字节是高位,长度不包括头部
// 第 7 个字节是类型
const char* header = buffer_.data();
const uint32_t a = static_cast<uint32_t>(header[4]) & 0xff;
const uint32_t b = static_cast<uint32_t>(header[5]) & 0xff;
const unsigned int type = header[6];
const uint32_t length = a | (b << 8);
if (kHeaderSize + length > buffer_.size()) { // length 不对劲,算一下居然比 buffer 还长
size_t drop_size = buffer_.size();
buffer_.clear();
if (!eof_) {
ReportCorruption(drop_size, "bad record length");
return kBadRecord;
}
// If the end of the file has been reached without reading |length| bytes
// of payload, assume the writer died in the middle of writing the record.
// Don't report a corruption.
// writer 写一半挂了,那么 reader 确实会读出怪 length,当作 EOF
return kEof;
}
if (type == kZeroType && length == 0) {
// Skip zero length record without reporting any drops since
// such records are produced by the mmap based writing code in
// env_posix.cc that preallocates file regions.
buffer_.clear();
return kBadRecord;
}
// Check crc
if (checksum_) {
// 前 4 个 Bytes 是 crc32
uint32_t expected_crc = crc32c::Unmask(DecodeFixed32(header));
// 跳过前6个字节,包括第7个字节(类型)一起计算数据部分的 crc32
uint32_t actual_crc = crc32c::Value(header + 6, 1 + length);
if (actual_crc != expected_crc) {
// Drop the rest of the buffer since "length" itself may have
// been corrupted and if we trust it, we could find some
// fragment of a real log record that just happens to look
// like a valid log record.
size_t drop_size = buffer_.size();
buffer_.clear();
ReportCorruption(drop_size, "checksum mismatch");
return kBadRecord;
}
}
// 跳过已经解析了内容
buffer_.remove_prefix(kHeaderSize + length);
// Skip physical record that started before initial_offset_
// 读到 initial_offset_ 之前的东西了
if (end_of_buffer_offset_ - buffer_.size() - kHeaderSize - length <
initial_offset_) {
result->clear();
return kBadRecord;
}
// result 指向 block data 部分
*result = Slice(header + kHeaderSize, length);
return type;
}
}
DumpTable
Status DumpTable(Env* env, const std::string& fname, WritableFile* dst) {
uint64_t file_size;
RandomAccessFile* file = nullptr; // 使用 RandomAccessFile 作为 backend
Table* table = nullptr;
Status s = env->GetFileSize(fname, &file_size);
if (s.ok()) {
s = env->NewRandomAccessFile(fname, &file);
}
if (s.ok()) {
// We use the default comparator, which may or may not match the
// comparator used in this database. However this should not cause
// problems since we only use Table operations that do not require
// any comparisons. In particular, we do not call Seek or Prev.
s = Table::Open(Options(), file, file_size, &table);
}
if (!s.ok()) {
delete table;
delete file;
return s;
}
ReadOptions ro;
ro.fill_cache = false; // 读取不会 cache
Iterator* iter = table->NewIterator(ro);
std::string r;
// 迭代写入 dst
for (iter->SeekToFirst(); iter->Valid(); iter->Next()) {
r.clear();
ParsedInternalKey key;
if (!ParseInternalKey(iter->key(), &key)) {
r = "badkey '";
AppendEscapedStringTo(&r, iter->key());
r += "' => '";
AppendEscapedStringTo(&r, iter->value());
r += "'\n";
dst->Append(r);
} else {
r = "'";
AppendEscapedStringTo(&r, key.user_key);
r += "' @ ";
AppendNumberTo(&r, key.sequence);
r += " : ";
// 删除也是一条记录
if (key.type == kTypeDeletion) {
r += "del";
} else if (key.type == kTypeValue) {
r += "val";
} else {
AppendNumberTo(&r, key.type);
}
r += " => '";
AppendEscapedStringTo(&r, iter->value());
r += "'\n";
dst->Append(r);
}
}
s = iter->status();
if (!s.ok()) {
dst->Append("iterator error: " + s.ToString() + "\n");
}
delete iter;
delete table;
delete file;
return Status::OK();
}
Format
- Table 中一些具体的组件
- BlockHandle:用于指向一个 block
- Footer:sstable 的 footer
- BlockContents:block 磁盘数据表示
定义
class Block;
class RandomAccessFile;
struct ReadOptions;
// BlockHandle is a pointer to the extent of a file that stores a data
// block or a meta block.
class BlockHandle {
public:
// Maximum encoding length of a BlockHandle
enum { kMaxEncodedLength = 10 + 10 };
BlockHandle();
// The offset of the block in the file.
uint64_t offset() const { return offset_; }
void set_offset(uint64_t offset) { offset_ = offset; }
// The size of the stored block
uint64_t size() const { return size_; }
void set_size(uint64_t size) { size_ = size; }
void EncodeTo(std::string* dst) const;
Status DecodeFrom(Slice* input);
private:
// 由文件的偏移和长度确定一个 handle
uint64_t offset_;
uint64_t size_;
};
// Footer encapsulates the fixed information stored at the tail
// end of every table file.
class Footer {
public:
// Encoded length of a Footer. Note that the serialization of a
// Footer will always occupy exactly this many bytes. It consists
// of two block handles and a magic number.
enum { kEncodedLength = 2 * BlockHandle::kMaxEncodedLength + 8 };
Footer() = default;
// The block handle for the metaindex block of the table
const BlockHandle& metaindex_handle() const { return metaindex_handle_; }
void set_metaindex_handle(const BlockHandle& h) { metaindex_handle_ = h; }
// The block handle for the index block of the table
const BlockHandle& index_handle() const { return index_handle_; }
void set_index_handle(const BlockHandle& h) { index_handle_ = h; }
void EncodeTo(std::string* dst) const;
Status DecodeFrom(Slice* input);
private:
// footer 由两个 index 的 handle 构成(还有一个 magic number 外加一些 padding)
BlockHandle metaindex_handle_;
BlockHandle index_handle_;
};
// kTableMagicNumber was picked by running
// echo http://code.google.com/p/leveldb/ | sha1sum
// and taking the leading 64 bits.
static const uint64_t kTableMagicNumber = 0xdb4775248b80fb57ull;
// 1-byte type + 32-bit crc
static const size_t kBlockTrailerSize = 5;
struct BlockContents {
Slice data; // Actual contents of data
bool cachable; // True if data can be cached
bool heap_allocated; // True if caller should delete[] data.data()
};
// Read the block identified by "handle" from "file". On failure
// return non-OK. On success fill *result and return OK.
Status ReadBlock(RandomAccessFile* file, const ReadOptions& options,
const BlockHandle& handle, BlockContents* result);
实现
void BlockHandle::EncodeTo(std::string* dst) const {
// Sanity check that all fields have been set
assert(offset_ != ~static_cast<uint64_t>(0));
assert(size_ != ~static_cast<uint64_t>(0));
// 变长编码,但又有 padding,不知道它们是怎么想的,大概是为了兼容吧,也许哪一天 u64 也装不下了呢?如果拓展的话使用固定长度编码的旧 table 就会读不出来
PutVarint64(dst, offset_);
PutVarint64(dst, size_);
}
Status BlockHandle::DecodeFrom(Slice* input) {
// 变长编码
if (GetVarint64(input, &offset_) && GetVarint64(input, &size_)) {
return Status::OK();
} else {
return Status::Corruption("bad block handle");
}
}
void Footer::EncodeTo(std::string* dst) const {
const size_t original_size = dst->size();
metaindex_handle_.EncodeTo(dst);
index_handle_.EncodeTo(dst);
dst->resize(2 * BlockHandle::kMaxEncodedLength); // Padding
// 小端编码 magic number,怪
PutFixed32(dst, static_cast<uint32_t>(kTableMagicNumber & 0xffffffffu));
PutFixed32(dst, static_cast<uint32_t>(kTableMagicNumber >> 32));
// 会写进入 48 个 Bytes
assert(dst->size() == original_size + kEncodedLength);
(void)original_size; // Disable unused variable warning.
}
Status Footer::DecodeFrom(Slice* input) {
if (input->size() < kEncodedLength) {
return Status::Corruption("not an sstable (footer too short)");
}
const char* magic_ptr = input->data() + kEncodedLength - 8;
const uint32_t magic_lo = DecodeFixed32(magic_ptr);
const uint32_t magic_hi = DecodeFixed32(magic_ptr + 4);
const uint64_t magic = ((static_cast<uint64_t>(magic_hi) << 32) |
(static_cast<uint64_t>(magic_lo)));
if (magic != kTableMagicNumber) {
return Status::Corruption("not an sstable (bad magic number)");
}
Status result = metaindex_handle_.DecodeFrom(input);
if (result.ok()) {
result = index_handle_.DecodeFrom(input);
}
if (result.ok()) {
// We skip over any leftover data (just padding for now) in "input"
const char* end = magic_ptr + 8;
*input = Slice(end, input->data() + input->size() - end);
}
return result;
}
Status ReadBlock(RandomAccessFile* file, const ReadOptions& options,
const BlockHandle& handle, BlockContents* result) {
result->data = Slice();
result->cachable = false;
result->heap_allocated = false;
// Read the block contents as well as the type/crc footer.
// See table_builder.cc for the code that built this structure.
size_t n = static_cast<size_t>(handle.size());
// trailer 的大小不算在 handle 的 size 里...
char* buf = new char[n + kBlockTrailerSize];
Slice contents; // 可能是 buf 的一段切片,可能也不是(mmap 的 file 则不是)
Status s = file->Read(handle.offset(), n + kBlockTrailerSize, &contents, buf);
if (!s.ok()) {
delete[] buf;
return s;
}
if (contents.size() != n + kBlockTrailerSize) {
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("truncated block read");
}
// Check the crc of the type and the block contents
const char* data = contents.data(); // Pointer to where Read put the data
if (options.verify_checksums) {
const uint32_t crc = crc32c::Unmask(DecodeFixed32(data + n + 1));
const uint32_t actual = crc32c::Value(data, n + 1);
if (actual != crc) {
delete[] buf;
s = Status::Corruption("block checksum mismatch");
return s;
}
}
switch (data[n]) { // 最后一个是 data block 的 type
case kNoCompression:
if (data != buf) {
// File implementation gave us pointer to some other data.
// Use it directly under the assumption that it will be live
// while the file is open.
// 这里发现 data 没有指向 buf,说明 file->Read 是读到了一个 mmap file 了,没有拷贝到 buf 里
delete[] buf; // 那么 buf 显然是没用了,删了
result->data = Slice(data, n);
result->heap_allocated = false; // 没有进一步分配堆内存
// mmap file 操作系统有 page cache,所以不用再 cache 一次了
result->cachable = false; // Do not double-cache
} else {
// 这里则是正常的 file io,拷贝到了 buf 里
result->data = Slice(buf, n);
result->heap_allocated = true; // 进行了一次堆内存分配
result->cachable = true; // 这里做 cache
}
// Ok
break;
case kSnappyCompression: {
size_t ulength = 0;
// 先估计一下解压后大概有多大
if (!port::Snappy_GetUncompressedLength(data, n, &ulength)) {
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted snappy compressed block length");
}
char* ubuf = new char[ulength];
// 解压
if (!port::Snappy_Uncompress(data, n, ubuf)) {
delete[] buf;
delete[] ubuf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted snappy compressed block contents");
}
delete[] buf;
result->data = Slice(ubuf, ulength);
result->heap_allocated = true; // 解压缩一定会分配堆内存
result->cachable = true; // 为解压缩过后的数据做 cache
break;
}
case kZstdCompression: {
// 类似
size_t ulength = 0;
if (!port::Zstd_GetUncompressedLength(data, n, &ulength)) {
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted zstd compressed block length");
}
char* ubuf = new char[ulength];
if (!port::Zstd_Uncompress(data, n, ubuf)) {
delete[] buf;
delete[] ubuf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted zstd compressed block contents");
}
delete[] buf;
result->data = Slice(ubuf, ulength);
result->heap_allocated = true;
result->cachable = true;
break;
}
default:
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("bad block type");
}
return Status::OK();
}
Table::Open
Table 定义
- 主要有
Open和NewIterator两个常用的方法
// A Table is a sorted map from strings to strings. Tables are
// immutable and persistent. A Table may be safely accessed from
// multiple threads without external synchronization.
class LEVELDB_EXPORT Table {
public:
// Attempt to open the table that is stored in bytes [0..file_size)
// of "file", and read the metadata entries necessary to allow
// retrieving data from the table.
//
// If successful, returns ok and sets "*table" to the newly opened
// table. The client should delete "*table" when no longer needed.
// If there was an error while initializing the table, sets "*table"
// to nullptr and returns a non-ok status. Does not take ownership of
// "*source", but the client must ensure that "source" remains live
// for the duration of the returned table's lifetime.
//
// *file must remain live while this Table is in use.
static Status Open(const Options& options, RandomAccessFile* file,
uint64_t file_size, Table** table);
Table(const Table&) = delete;
Table& operator=(const Table&) = delete;
~Table();
// Returns a new iterator over the table contents.
// The result of NewIterator() is initially invalid (caller must
// call one of the Seek methods on the iterator before using it).
Iterator* NewIterator(const ReadOptions&) const;
// Given a key, return an approximate byte offset in the file where
// the data for that key begins (or would begin if the key were
// present in the file). The returned value is in terms of file
// bytes, and so includes effects like compression of the underlying data.
// E.g., the approximate offset of the last key in the table will
// be close to the file length.
uint64_t ApproximateOffsetOf(const Slice& key) const;
private:
friend class TableCache;
struct Rep;
static Iterator* BlockReader(void*, const ReadOptions&, const Slice&);
explicit Table(Rep* rep) : rep_(rep) {}
// Calls (*handle_result)(arg, ...) with the entry found after a call
// to Seek(key). May not make such a call if filter policy says
// that key is not present.
Status InternalGet(const ReadOptions&, const Slice& key, void* arg,
void (*handle_result)(void* arg, const Slice& k,
const Slice& v));
void ReadMeta(const Footer& footer);
void ReadFilter(const Slice& filter_handle_value);
Rep* const rep_;
};
Table::Open 实现
/// Table 的底层表示
struct Table::Rep {
~Rep() {
delete filter;
delete[] filter_data;
delete index_block;
}
Options options;
Status status;
RandomAccessFile* file;
uint64_t cache_id;
// Filter meta block 相关,默认是布隆过滤器
FilterBlockReader* filter;
// Filter data,过滤器的存储
const char* filter_data;
// meta block 的 index
BlockHandle metaindex_handle; // Handle to metaindex_block: saved from footer
// data block 的 index
Block* index_block;
};
Status Table::Open(const Options& options, RandomAccessFile* file,
uint64_t size, Table** table) {
*table = nullptr;
if (size < Footer::kEncodedLength) {
return Status::Corruption("file is too short to be an sstable");
}
// 倒着读,先读 footer
char footer_space[Footer::kEncodedLength];
Slice footer_input;
Status s = file->Read(size - Footer::kEncodedLength, Footer::kEncodedLength,
&footer_input, footer_space);
if (!s.ok()) return s;
Footer footer;
s = footer.DecodeFrom(&footer_input);
if (!s.ok()) return s;
// 然后读 data block 的 index
// Read the index block
BlockContents index_block_contents;
ReadOptions opt;
if (options.paranoid_checks) { // 积极的 checksum 可能会导致一整个 sstable 打不开
opt.verify_checksums = true;
}
// 从 footer 里记载的 index block 的 handle 那里找到 index
s = ReadBlock(file, opt, footer.index_handle(), &index_block_contents);
if (s.ok()) {
// We've successfully read the footer and the index block: we're
// ready to serve requests.
Block* index_block = new Block(index_block_contents);
Rep* rep = new Table::Rep;
rep->options = options;
rep->file = file;
rep->metaindex_handle = footer.metaindex_handle();
rep->index_block = index_block;
// 0 表示不开启 cache
rep->cache_id = (options.block_cache ? options.block_cache->NewId() : 0);
rep->filter_data = nullptr;
rep->filter = nullptr;
*table = new Table(rep);
// 最后读 meta block
(*table)->ReadMeta(footer);
}
return s;
}
Table::ReadMeta 实现
void Table::ReadMeta(const Footer& footer) {
// 目前只有一个 filter meta block
if (rep_->options.filter_policy == nullptr) {
return; // Do not need any metadata
}
// TODO(sanjay): Skip this if footer.metaindex_handle() size indicates
// it is an empty block.
ReadOptions opt;
if (rep_->options.paranoid_checks) {
opt.verify_checksums = true;
}
BlockContents contents;
if (!ReadBlock(rep_->file, opt, footer.metaindex_handle(), &contents).ok()) {
// Do not propagate errors since meta info is not needed for operation
return;
}
// 创建内存中的 Block 数据表示
Block* meta = new Block(contents);
Iterator* iter = meta->NewIterator(BytewiseComparator());
std::string key = "filter.";
key.append(rep_->options.filter_policy->Name()); // 默认 leveldb.BuiltinBloomFilter2
iter->Seek(key);
if (iter->Valid() && iter->key() == Slice(key)) {
ReadFilter(iter->value()); // 只会读 filter
}
delete iter;
delete meta;
}
void Table::ReadFilter(const Slice& filter_handle_value) {
Slice v = filter_handle_value;
BlockHandle filter_handle;
// meta handle 里存的也是一个 BlockHandle
if (!filter_handle.DecodeFrom(&v).ok()) {
return;
}
// We might want to unify with ReadBlock() if we start
// requiring checksum verification in Table::Open.
ReadOptions opt;
if (rep_->options.paranoid_checks) {
opt.verify_checksums = true;
}
BlockContents block;
if (!ReadBlock(rep_->file, opt, filter_handle, &block).ok()) {
return;
}
if (block.heap_allocated) {
// 记录一下,Table 被 delete 了也能顺带着把对应分配的堆内存给回收了
rep_->filter_data = block.data.data(); // Will need to delete later
}
// 创建 Filter
rep_->filter = new FilterBlockReader(rep_->options.filter_policy, block.data);
}
FilterBlockReader
- 内存的 Filter 数据表示
- 默认是有多个布隆过滤器组成
定义
class FilterPolicy;
class FilterBlockReader {
public:
// REQUIRES: "contents" and *policy must stay live while *this is live.
FilterBlockReader(const FilterPolicy* policy, const Slice& contents);
bool KeyMayMatch(uint64_t block_offset, const Slice& key);
private:
const FilterPolicy* policy_;
const char* data_; // Pointer to filter data (at block-start)
const char* offset_; // Pointer to beginning of offset array (at block-end)
size_t num_; // Number of entries in offset array
size_t base_lg_; // Encoding parameter (see kFilterBaseLg in .cc file)
};
实现
FilterBlockReader::FilterBlockReader(const FilterPolicy* policy,
const Slice& contents)
: policy_(policy), data_(nullptr), offset_(nullptr), num_(0), base_lg_(0) {
size_t n = contents.size();
// 长度小于 5 说明有问题
if (n < 5) return; // 1 byte for base_lg_ and 4 for start of offset array
base_lg_ = contents[n - 1];
uint32_t last_word = DecodeFixed32(contents.data() + n - 5);
if (last_word > n - 5) return; // 第一个 offset 所在的位置不应该比读出来的 length 更长
data_ = contents.data();
offset_ = data_ + last_word;
num_ = (n - 5 - last_word) / 4; // 每个 offset entry 都是 4B,这里一共有多少个 offset
}
bool FilterBlockReader::KeyMayMatch(uint64_t block_offset, const Slice& key) {
uint64_t index = block_offset >> base_lg_; // 查看这个 block 应该落到哪个 filter 中
if (index < num_) {
// 每个 offset 存两个数,用于指示 data 中哪块是一个完整的 filter data
uint32_t start = DecodeFixed32(offset_ + index * 4);
uint32_t limit = DecodeFixed32(offset_ + index * 4 + 4);
if (start <= limit && limit <= static_cast<size_t>(offset_ - data_)) { // limit 应该指向 offset 的前面
Slice filter = Slice(data_ + start, limit - start);
return policy_->KeyMayMatch(key, filter); // 跳到对应的 filter policy 中
} else if (start == limit) {
// Empty filters do not match any keys
// 空的 filter data,说明没有创建任何 filter,也就是说没有 key
return false;
}
}
// 误报,当作过滤器失效
return true; // Errors are treated as potential matches
}
Table::NewIterator
Table::NewIterator 实现
Iterator* Table::NewIterator(const ReadOptions& options) const {
// 两层的 iterator,先查 index,再查 block
// block 的 iterator 是动态创建的,只有读到对应的 block 才会创建对应的 iterator
return NewTwoLevelIterator(
rep_->index_block->NewIterator(rep_->options.comparator),
&Table::BlockReader, const_cast<Table*>(this), options);
}
// Convert an index iterator value (i.e., an encoded BlockHandle)
// into an iterator over the contents of the corresponding block.
// Index => Block
Iterator* Table::BlockReader(void* arg, const ReadOptions& options,
const Slice& index_value) {
Table* table = reinterpret_cast<Table*>(arg);
Cache* block_cache = table->rep_->options.block_cache;
Block* block = nullptr;
Cache::Handle* cache_handle = nullptr;
BlockHandle handle;
Slice input = index_value;
Status s = handle.DecodeFrom(&input);
// We intentionally allow extra stuff in index_value so that we
// can add more features in the future.
if (s.ok()) {
BlockContents contents;
if (block_cache != nullptr) {
char cache_key_buffer[16];
EncodeFixed64(cache_key_buffer, table->rep_->cache_id); // cache id 会作为 cache key 的开头
EncodeFixed64(cache_key_buffer + 8, handle.offset()); // 其次是它的 offset,可以唯一确定一个 block
Slice key(cache_key_buffer, sizeof(cache_key_buffer));
cache_handle = block_cache->Lookup(key);
if (cache_handle != nullptr) {
// 命中了 cache
block = reinterpret_cast<Block*>(block_cache->Value(cache_handle));
} else {
s = ReadBlock(table->rep_->file, options, handle, &contents);
if (s.ok()) {
block = new Block(contents);
// fill_cache 在这里参与控制这次 read 会不会存入 cache
if (contents.cachable && options.fill_cache) {
cache_handle = block_cache->Insert(key, block, block->size(),
&DeleteCachedBlock);
}
}
}
} else {
s = ReadBlock(table->rep_->file, options, handle, &contents);
if (s.ok()) {
block = new Block(contents);
}
}
}
Iterator* iter;
if (block != nullptr) {
iter = block->NewIterator(table->rep_->options.comparator); // 关键的部分,跳到 Block 中的 iterator
// 根据 block 的 backend 来确定如何回收 block
if (cache_handle == nullptr) {
iter->RegisterCleanup(&DeleteBlock, block, nullptr);
} else {
iter->RegisterCleanup(&ReleaseBlock, block_cache, cache_handle);
}
} else {
// 为了保证接口的整洁...
iter = NewErrorIterator(s);
}
return iter;
}
// 传给 Iterator 的回调,没有从 cache 里读的情况下会清理 block
static void DeleteBlock(void* arg, void* ignored) {
delete reinterpret_cast<Block*>(arg);
}
// 传给 Iterator 的回调,从 cache 里读的话把 cache handle release 掉,生命周期归还 cache 管理
static void ReleaseBlock(void* arg, void* h) {
Cache* cache = reinterpret_cast<Cache*>(arg);
Cache::Handle* handle = reinterpret_cast<Cache::Handle*>(h);
cache->Release(handle);
}
// 传给 Cache 的回调,淘汰时会清理 block
static void DeleteCachedBlock(const Slice& key, void* value) {
Block* block = reinterpret_cast<Block*>(value);
delete block;
}
Block
- 内存中的 block 数据表示
定义
class Block {
public:
// Initialize the block with the specified contents.
// 是由磁盘中的 BlockContents 表示转换而来的
explicit Block(const BlockContents& contents);
Block(const Block&) = delete;
Block& operator=(const Block&) = delete;
~Block();
size_t size() const { return size_; }
Iterator* NewIterator(const Comparator* comparator); // 主要使用的方法
private:
class Iter;
uint32_t NumRestarts() const;
const char* data_;
size_t size_;
uint32_t restart_offset_; // Offset in data_ of restart array
bool owned_; // Block owns data_[],对应 BlockContents heap_allocated
};
实现
inline uint32_t Block::NumRestarts() const {
assert(size_ >= sizeof(uint32_t));
// 注意到这里的 block contents 去掉了最后的 crc32 和 type 了,所以随后 4B 是 num_restarts
// 用于算出 restarts 从哪开始
return DecodeFixed32(data_ + size_ - sizeof(uint32_t));
}
Block::Block(const BlockContents& contents)
: data_(contents.data.data()),
size_(contents.data.size()),
owned_(contents.heap_allocated) {
if (size_ < sizeof(uint32_t)) {
size_ = 0; // Error marker
} else {
size_t max_restarts_allowed = (size_ - sizeof(uint32_t)) / sizeof(uint32_t);
if (NumRestarts() > max_restarts_allowed) {
// The size is too small for NumRestarts()
size_ = 0;
} else {
restart_offset_ = size_ - (1 + NumRestarts()) * sizeof(uint32_t);
}
}
}
Block::~Block() {
if (owned_) { // 内存管理
delete[] data_;
}
}
// Helper routine: decode the next block entry starting at "p",
// storing the number of shared key bytes, non_shared key bytes,
// and the length of the value in "*shared", "*non_shared", and
// "*value_length", respectively. Will not dereference past "limit".
//
// If any errors are detected, returns nullptr. Otherwise, returns a
// pointer to the key delta (just past the three decoded values).
static inline const char* DecodeEntry(const char* p, const char* limit,
uint32_t* shared, uint32_t* non_shared,
uint32_t* value_length) {
if (limit - p < 3) return nullptr;
*shared = reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(p)[0];
*non_shared = reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(p)[1];
*value_length = reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(p)[2];
if ((*shared | *non_shared | *value_length) < 128) {
// Fast path: all three values are encoded in one byte each
p += 3;
} else {
if ((p = GetVarint32Ptr(p, limit, shared)) == nullptr) return nullptr;
if ((p = GetVarint32Ptr(p, limit, non_shared)) == nullptr) return nullptr;
if ((p = GetVarint32Ptr(p, limit, value_length)) == nullptr) return nullptr;
}
if (static_cast<uint32_t>(limit - p) < (*non_shared + *value_length)) {
return nullptr;
}
return p;
}
class Block::Iter : public Iterator {
private:
const Comparator* const comparator_;
const char* const data_; // underlying block contents
uint32_t const restarts_; // Offset of restart array (list of fixed32)
uint32_t const num_restarts_; // Number of uint32_t entries in restart array
// current_ is offset in data_ of current entry. >= restarts_ if !Valid
uint32_t current_;
uint32_t restart_index_; // Index of restart block in which current_ falls
std::string key_;
Slice value_;
Status status_;
inline int Compare(const Slice& a, const Slice& b) const {
return comparator_->Compare(a, b);
}
// Return the offset in data_ just past the end of the current entry.
inline uint32_t NextEntryOffset() const {
return (value_.data() + value_.size()) - data_;
}
uint32_t GetRestartPoint(uint32_t index) {
assert(index < num_restarts_);
return DecodeFixed32(data_ + restarts_ + index * sizeof(uint32_t));
}
void SeekToRestartPoint(uint32_t index) {
key_.clear();
restart_index_ = index;
// current_ will be fixed by ParseNextKey();
// ParseNextKey() starts at the end of value_, so set value_ accordingly
uint32_t offset = GetRestartPoint(index);
value_ = Slice(data_ + offset, 0);
}
public:
Iter(const Comparator* comparator, const char* data, uint32_t restarts,
uint32_t num_restarts)
: comparator_(comparator),
data_(data),
restarts_(restarts),
num_restarts_(num_restarts),
current_(restarts_),
restart_index_(num_restarts_) {
assert(num_restarts_ > 0);
}
bool Valid() const override { return current_ < restarts_; }
Status status() const override { return status_; }
Slice key() const override {
assert(Valid());
return key_;
}
Slice value() const override {
assert(Valid());
return value_;
}
void Next() override {
assert(Valid());
ParseNextKey();
}
void Prev() override {
assert(Valid());
// Scan backwards to a restart point before current_
const uint32_t original = current_;
while (GetRestartPoint(restart_index_) >= original) {
if (restart_index_ == 0) {
// No more entries
current_ = restarts_;
restart_index_ = num_restarts_;
return;
}
restart_index_--;
}
SeekToRestartPoint(restart_index_);
do {
// Loop until end of current entry hits the start of original entry
} while (ParseNextKey() && NextEntryOffset() < original);
}
void Seek(const Slice& target) override {
// 最爱的二分(
// Binary search in restart array to find the last restart point
// with a key < target
uint32_t left = 0;
uint32_t right = num_restarts_ - 1;
int current_key_compare = 0;
// 先粗略的二分一下,从 restarts 那里找到位置
if (Valid()) {
// If we're already scanning, use the current position as a starting
// point. This is beneficial if the key we're seeking to is ahead of the
// current position.
current_key_compare = Compare(key_, target);
if (current_key_compare < 0) {
// key_ is smaller than target
left = restart_index_;
} else if (current_key_compare > 0) {
right = restart_index_;
} else {
// We're seeking to the key we're already at.
return;
}
}
// 细致的二分
while (left < right) {
uint32_t mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
uint32_t region_offset = GetRestartPoint(mid);
uint32_t shared, non_shared, value_length;
const char* key_ptr =
DecodeEntry(data_ + region_offset, data_ + restarts_, &shared,
&non_shared, &value_length);
if (key_ptr == nullptr || (shared != 0)) {
CorruptionError();
return;
}
Slice mid_key(key_ptr, non_shared);
if (Compare(mid_key, target) < 0) {
// Key at "mid" is smaller than "target". Therefore all
// blocks before "mid" are uninteresting.
left = mid;
} else {
// Key at "mid" is >= "target". Therefore all blocks at or
// after "mid" are uninteresting.
right = mid - 1;
}
}
// We might be able to use our current position within the restart block.
// This is true if we determined the key we desire is in the current block
// and is after than the current key.
assert(current_key_compare == 0 || Valid());
bool skip_seek = left == restart_index_ && current_key_compare < 0;
if (!skip_seek) {
SeekToRestartPoint(left);
}
// Linear search (within restart block) for first key >= target
while (true) {
// restart 到位了就开始线性搜,这里可不可以用二分呢?似乎都是 key 是增量的形式不方便进行二分
if (!ParseNextKey()) {
return;
}
if (Compare(key_, target) >= 0) {
return;
}
}
}
void SeekToFirst() override {
SeekToRestartPoint(0);
ParseNextKey();
}
void SeekToLast() override {
SeekToRestartPoint(num_restarts_ - 1);
while (ParseNextKey() && NextEntryOffset() < restarts_) {
// Keep skipping
}
}
private:
void CorruptionError() {
current_ = restarts_;
restart_index_ = num_restarts_;
status_ = Status::Corruption("bad entry in block");
key_.clear();
value_.clear();
}
bool ParseNextKey() {
current_ = NextEntryOffset();
const char* p = data_ + current_;
const char* limit = data_ + restarts_; // Restarts come right after data
if (p >= limit) {
// No more entries to return. Mark as invalid.
current_ = restarts_;
restart_index_ = num_restarts_;
return false;
}
// Decode next entry
uint32_t shared, non_shared, value_length;
p = DecodeEntry(p, limit, &shared, &non_shared, &value_length);
if (p == nullptr || key_.size() < shared) {
CorruptionError();
return false;
} else {
key_.resize(shared);
key_.append(p, non_shared);
value_ = Slice(p + non_shared, value_length);
while (restart_index_ + 1 < num_restarts_ &&
GetRestartPoint(restart_index_ + 1) < current_) {
++restart_index_;
}
return true;
}
}
};
Iterator* Block::NewIterator(const Comparator* comparator) {
if (size_ < sizeof(uint32_t)) {
return NewErrorIterator(Status::Corruption("bad block contents"));
}
const uint32_t num_restarts = NumRestarts();
if (num_restarts == 0) {
return NewEmptyIterator();
} else {
return new Iter(comparator, data_, restart_offset_, num_restarts);
}
}
TwoLevelIterator
- 两层的 Iterator,一层 index,一层 block,根据 index iter动态更新 block iter
- 还能不能更高层呢?memtable!
typedef Iterator* (*BlockFunction)(void*, const ReadOptions&, const Slice&);
class TwoLevelIterator : public Iterator {
public:
TwoLevelIterator(Iterator* index_iter, BlockFunction block_function,
void* arg, const ReadOptions& options);
~TwoLevelIterator() override;
void Seek(const Slice& target) override;
void SeekToFirst() override;
void SeekToLast() override;
void Next() override;
void Prev() override;
bool Valid() const override { return data_iter_.Valid(); }
Slice key() const override {
assert(Valid());
return data_iter_.key();
}
Slice value() const override {
assert(Valid());
return data_iter_.value();
}
Status status() const override {
// It'd be nice if status() returned a const Status& instead of a Status
if (!index_iter_.status().ok()) {
return index_iter_.status();
} else if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr && !data_iter_.status().ok()) {
return data_iter_.status();
} else {
return status_;
}
}
private:
void SaveError(const Status& s) {
if (status_.ok() && !s.ok()) status_ = s;
}
void SkipEmptyDataBlocksForward();
void SkipEmptyDataBlocksBackward();
void SetDataIterator(Iterator* data_iter);
void InitDataBlock();
BlockFunction block_function_;
void* arg_;
const ReadOptions options_;
Status status_;
IteratorWrapper index_iter_; // IteratorWrapper 是 Iterator 的一层简单包装,提供了内部 iterator 的更新,缓存了valid_ 和 key_,更 cache friendly
IteratorWrapper data_iter_; // May be nullptr
// If data_iter_ is non-null, then "data_block_handle_" holds the
// "index_value" passed to block_function_ to create the data_iter_.
std::string data_block_handle_;
};
TwoLevelIterator::TwoLevelIterator(Iterator* index_iter,
BlockFunction block_function, void* arg,
const ReadOptions& options)
: block_function_(block_function),
arg_(arg),
options_(options),
index_iter_(index_iter),
data_iter_(nullptr) {}
TwoLevelIterator::~TwoLevelIterator() = default;
void TwoLevelIterator::Seek(const Slice& target) {
index_iter_.Seek(target);
InitDataBlock(); // 加载当前的 block
if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr) data_iter_.Seek(target);
SkipEmptyDataBlocksForward();
}
void TwoLevelIterator::SeekToFirst() {
index_iter_.SeekToFirst();
InitDataBlock();
if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr) data_iter_.SeekToFirst();
SkipEmptyDataBlocksForward();
}
void TwoLevelIterator::SeekToLast() {
index_iter_.SeekToLast();
InitDataBlock();
if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr) data_iter_.SeekToLast();
SkipEmptyDataBlocksBackward();
}
void TwoLevelIterator::Next() {
assert(Valid());
data_iter_.Next(); // Next 从底层 iter 开始,从上层开始可能会跳过某些 key
SkipEmptyDataBlocksForward();
}
void TwoLevelIterator::Prev() {
assert(Valid());
data_iter_.Prev(); // 类似 Next
SkipEmptyDataBlocksBackward();
}
// 往前跳过空的 data block
void TwoLevelIterator::SkipEmptyDataBlocksForward() {
while (data_iter_.iter() == nullptr || !data_iter_.Valid()) {
// Move to next block
if (!index_iter_.Valid()) {
SetDataIterator(nullptr);
return;
}
index_iter_.Next();
InitDataBlock();
if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr) data_iter_.SeekToFirst();
}
}
// 往后跳过空的 data block
void TwoLevelIterator::SkipEmptyDataBlocksBackward() {
while (data_iter_.iter() == nullptr || !data_iter_.Valid()) {
// Move to next block
if (!index_iter_.Valid()) {
SetDataIterator(nullptr);
return;
}
index_iter_.Prev();
InitDataBlock();
if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr) data_iter_.SeekToLast();
}
}
void TwoLevelIterator::SetDataIterator(Iterator* data_iter) {
if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr) SaveError(data_iter_.status());
data_iter_.Set(data_iter);
}
void TwoLevelIterator::InitDataBlock() {
if (!index_iter_.Valid()) {
SetDataIterator(nullptr);
} else {
Slice handle = index_iter_.value();
if (data_iter_.iter() != nullptr &&
handle.compare(data_block_handle_) == 0) {
// data_iter_ is already constructed with this iterator, so
// no need to change anything
// index 就是指向的当前的 block,不用修改了
} else {
Iterator* iter = (*block_function_)(arg_, options_, handle);
data_block_handle_.assign(handle.data(), handle.size());
SetDataIterator(iter);
}
}
}
Writer
写到这里发现内容有点多了,Writer 相比 Reader 的内容相对少一些(没有 Cache,Iterator 啥的),相信看完 Reader 实现的你也能想到 Writer 是怎么实现了的吧(
Conclusion
可以看出有不少 C++ 工程上的技巧,同时也可以看出 C++ 工程需要构思好对象的所有权管理才不会导致 double free/leak 等问题
代码质量良好,很少令人迷惑的片段,不过还是可以进一步打磨的,一些方法参数可以变得简单一点