有序数据结构,所有的操作都是 log(N),有随机过程,易于实现(所以也易于改造成无锁并发,例如:crossbeam-skiplist)
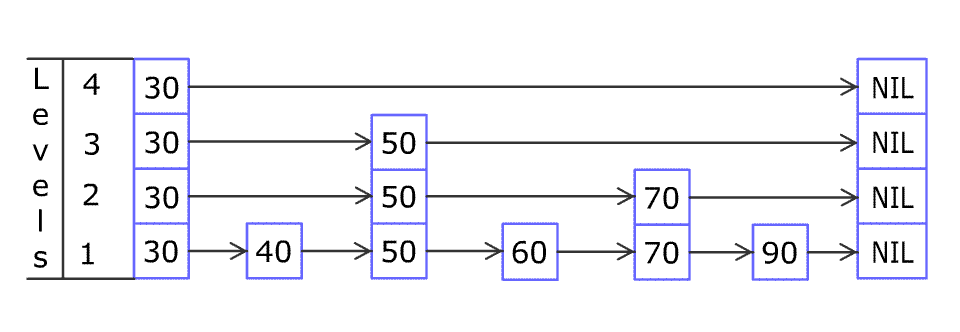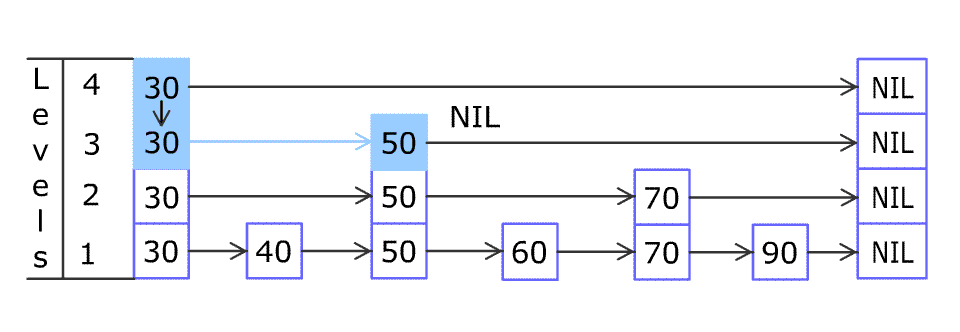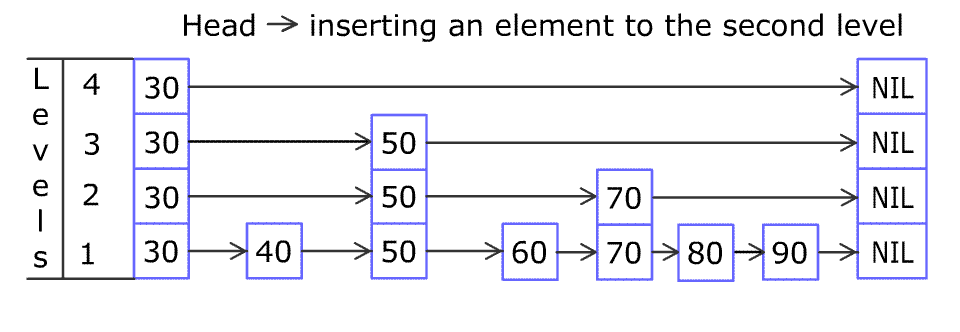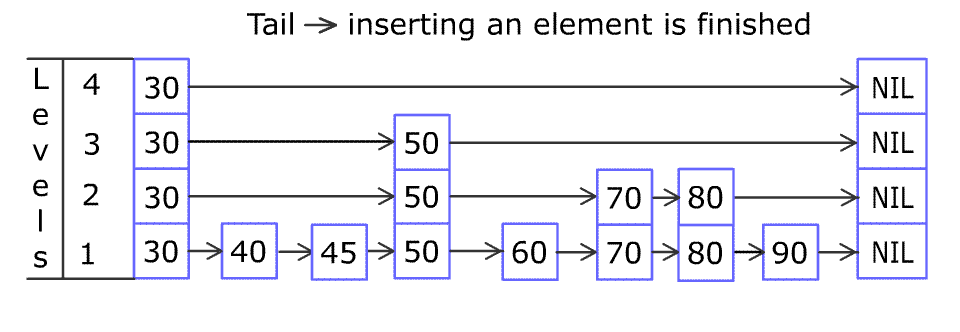
- 图示
- 层级从低向高编号,从最高层开始迭代

- 插入示例
- Coin flip,有概率向上增长,这样查询的速度就会变快
- 概率不应该过高或者过低
- 过高显然会有更多链接,耗费更多内存
- 过低查找效率比较低
- 如果从 1 开始每次向上再增长一层的概率相等且为 $t$ 的话,认为每次都有 $p=1-t$ 的概率停止生长,那么在第 k 次停止生长的概率为 $(1-p)^{(k-1)}p$,此时的高度是 k,服从均值为 $\frac{1}{p}$,方差为 $\sigma^2 = \frac{1-p}{p^2}$ 的几何分布。记第 i 次增长后的高度为随机变量 $X_i$,那么对于 n 次插入,平均每个节点的高度为 $\bar{X} = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^nX_i$;当 n 比较大时,由中心极限定理,$\bar{X}$ 服从均值为 $\mu = \frac{1}{p}$ 方差为 $\sigma^2 = \frac{1-p}{np^2}$ 的正态分布。
- 即平均而言,每个节点会出现在 $\frac{1}{p} = \frac{1}{1-t}$ 层中。
- 概率不应该过高或者过低
特征
- Arena 内存管理
- 允许多个读和一个写入并发
- 外部保证:
- 多个写入时保证互斥与同步
- 正在读时 SkipList 不能被删除
Invariants:
- 分配的 Node 在整个 SkipList 被删之前永远不会被删除
- Node 中的字段除了 prev/next 指针以外,插入到跳表里之后不会改变
- 只有 Insert() 会改变跳表,并且原子操作会使用 Release 级别的 Ordering 确保写入会被其他线程观察到
定义
- SkipList 定义:
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
class SkipList {
private:
// 节点,实现里面定义了结构
struct Node;
public:
// Create a new SkipList object that will use "cmp" for comparing keys,
// and will allocate memory using "*arena". Objects allocated in the arena
// must remain allocated for the lifetime of the skiplist object.
// arena 需要保证 SkipList 没删之前不会被删除
explicit SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena);
// 删掉了拷贝和赋值构造,只允许引用传递
SkipList(const SkipList&) = delete;
SkipList& operator=(const SkipList&) = delete;
// Insert key into the list.
// REQUIRES: nothing that compares equal to key is currently in the list.
void Insert(const Key& key);
// Returns true iff an entry that compares equal to key is in the list.
bool Contains(const Key& key) const;
private:
// 最大高度限制是 12
enum { kMaxHeight = 12 };
inline int GetMaxHeight() const {
return max_height_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
Node* NewNode(const Key& key, int height);
int RandomHeight();
bool Equal(const Key& a, const Key& b) const { return (compare_(a, b) == 0); }
// Return true if key is greater than the data stored in "n"
bool KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const;
// Return the earliest node that comes at or after key.
// Return nullptr if there is no such node.
//
// If prev is non-null, fills prev[level] with pointer to previous
// node at "level" for every level in [0..max_height_-1].
//
// 找后继,并记录查找过程中每一层的前驱到 prev 中,如果提前在某一层找到和 key 相等的节点的话,这不会停止,而是继续记录 prev
Node* FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev) const;
// Return the latest node with a key < key.
// Return head_ if there is no such node.
// 找到 key 的前驱并返回
Node* FindLessThan(const Key& key) const;
// Return the last node in the list.
// Return head_ if list is empty.
Node* FindLast() const;
// Immutable after construction
Comparator const compare_;
Arena* const arena_; // Arena used for allocations of nodes
// dummy 头节点,它出现在所有层
Node* const head_;
// Modified only by Insert(). Read racily by readers, but stale
// values are ok.
// 允许 reader 读出旧值
// 最高的那个节点的高度,比这个还高的节点在插入时,高出的部分的前驱就是 dummy head 了
std::atomic<int> max_height_; // Height of the entire list
// Read/written only by Insert().
Random rnd_;
};
- Iterator 定义
- 除了基本的 Prev/Next 还可以 Seek 到给定的地方
// Iteration over the contents of a skip list
class Iterator {
public:
// Initialize an iterator over the specified list.
// The returned iterator is not valid.
explicit Iterator(const SkipList* list);
// Returns true if the iterator is positioned at a valid node.
bool Valid() const;
// Returns the key at the current position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
const Key& key() const;
// Advances to the next position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Next();
// Advances to the previous position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Prev();
// Advance to the first entry with a key >= target
// 找到 target 或者其的后继
void Seek(const Key& target);
// Position at the first entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToFirst();
// Position at the last entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToLast();
private:
const SkipList* list_;
Node* node_;
// Intentionally copyable
};
实现
- Node 定义
组成:
- 一个固定的 Key
- 每层的下一个节点(动态大小)
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) {}
// 一个固定的 key
Key const key;
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
// 找到某一层的后继
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
// acquire 确保原子读操作能看见最新的写入
return next_[n].load(std::memory_order_acquire);
}
// 设置某一层的后继
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
// 相对的,这里写入用 release 确保最新写入会被观察到
next_[n].store(x, std::memory_order_release);
}
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
// 一点点的性能提升,对于不要求线性读的话,只提供原子操作保证
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return next_[n].load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
// 类似,只提供原子操作保证
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].store(x, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
// 堆叠起来的 _next 指针
// 数组的长度表示这个节点出现在哪些层,注意这个大小 1 是假的,实际需要按照它具体的层级来分配内存
// 数组的内容是它出现的每一层的下一个节点是什么
std::atomic<Node*> next_[1];
};
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key, Comparator>::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) {
// 对齐动态分配大小,按照层的高度,next_ 也会有不同的大小
char* const node_memory = arena_->AllocateAligned(sizeof(Node) + sizeof(std::atomic<Node*>) * (height - 1));
// new [dst] Type(...) 语法,在 dst 中构造类型,不会分配内存
return new (node_memory) Node(key);
}
- Iterator
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::Iterator(const SkipList* list) {
list_ = list;
node_ = nullptr;
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline bool SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::Valid() const {
return node_ != nullptr;
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline const Key& SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::key() const {
assert(Valid()); // 确保每次都是 valid
return node_->key;
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::Next() {
assert(Valid());
// 为了保证迭代器不会跳过一些节点,所以要按所有节点都出现的最底层遍历。
node_ = node_->Next(0);
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::Prev() {
// Instead of using explicit "prev" links, we just search for the
// last node that falls before key.
// 没有 prev 指针,从 skip list 找前驱,然后移动过去,这个操作是 O(logN) 的,而不是 Next 的 O(1)
assert(Valid());
node_ = list_->FindLessThan(node_->key);
if (node_ == list_->head_) {
node_ = nullptr;
}
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::Seek(const Key& target) {
// 找到后继并移动过去
node_ = list_->FindGreaterOrEqual(target, nullptr);
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::SeekToFirst() {
// dummy head 的后面一个就是第一个
node_ = list_->head_->Next(0);
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator::SeekToLast() {
node_ = list_->FindLast();
if (node_ == list_->head_) {
node_ = nullptr;
}
}
- SkipList
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key, Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
// 从 1 开始,每 1/4 的概率会增高,最大不会超过 kMaxHeight=12
// 如果认为每次都有 3/4 的概率停止生长,那么在第 k 次停止生长的概率为 (1-3/4)^(k-1) * 3/4,此时的高度是 k
// 则生长的高度 x = k 服从几何分布
int height = 1;
while (height < kMaxHeight && rnd_.OneIn(kBranching)) {
height++;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key, Comparator>::KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const {
// null n is considered infinite
// 空指针表示无穷大,那么某一层最后一个节点,它的 next(nullptr) 肯定比任何 key 都大,这样总会下降到下一层去查找。
return (n != nullptr) && (compare_(n->key, key) < 0);
}
// 找后继,并记录查找过程中每一层的前驱到 prev 中
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key,
Node** prev) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1; // 从最高层开始
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// 如果 key 比 next->key 大,从 next 开始继续在这一层找
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {
// key 小于或者等于 next->key 了,可能是 next 是 nullptr 了,也可能是上一层 x 到 x->next 之间有 gap,需要到下一层继续找。
if (prev != nullptr) prev[level] = x; // 记录一下上一层找到的前驱 x
if (level == 0) {
// 它会找到最底层,而不是在某一层找到相等的并退出,因为它要记录每一层的 prev
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--; // 到下一层找
}
}
}
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindLessThan(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1; // 从最高层开始
while (true) {
assert(x == head_ || compare_(x->key, key) < 0); // loop invariants: 如果不是空 list 的话,x->key 总小于 key
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == nullptr || compare_(next->key, key) >= 0) {
// x 这层的下一个如果比 key 要大时,可能有 gap,下降到下一层查找
if (level == 0) {
// 这里是找前驱,所以必须下降到最底层,不然谁也不知道上层找到的前驱到 key 是不是有 gap
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--; // 到下一层找
}
} else {
// 这一层里找到了比 x 更接近 key 的前驱,跳过 gap 移动到这个节点继续寻找。
x = next;
}
}
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindLast()
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1; // 从最高层开始
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == nullptr) { // 直到找到这一层的末尾
if (level == 0) {
// 类似 FindLessThan(key::MAX),所以必须下降到最底层
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--; // 到下一层找
}
} else {
// 如果不是这层的末尾则继续后找
x = next;
}
}
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena)
: compare_(cmp), // 自定义的比较器
arena_(arena),
head_(NewNode(0 /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)), // dummy head,出现在所有层
max_height_(1),
rnd_(0xdeadbeef) { // deedbeef~
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
head_->SetNext(i, nullptr); // dummy head,每一层的下一个先置空
}
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized. 偷性能(
Node* prev[kMaxHeight]; // 插入时记录每一层的前驱,方便后面增长时设置前驱的指针
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev); // 找后继,但其实主要是找每层的前驱,注意这只会插入 prev[0:max_height_]
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
// 不允许找到和 key 相同的 x,即不允许重复 key
assert(x == nullptr || !Equal(key, x->key));
int height = RandomHeight();
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
// 如果比当前最高的节点还高,那更高的链接中的前驱就是 dummy head 了
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (nullptr), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since nullptr sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
//
// 记录当前节点的高度为最大高度
// 这里没有用更严格的内存序,允许 reader 读到旧的的 max_height_
// 当 reader 读到旧的 max_height_ 时,它将会从比较低的层级往下查找,可能会遇到当前插入的节点
// 当 reader 读到新的 max_height_ 时,它将会从更高层开始往下查找
// 1. 它在更高层遇到了当前插入的节点,那么它可以通过这个节点跳过一些节点,或者发现这个节点就是要找的节点
// 2. 它没有在更高层但没有看见新插入的节点,它发现 head_[max_height_-1] 后面就是 nullptr,就直接掉到下面的层级里查找了,它可能会在下面的层级里继续遇到当前插入的节点,那么情况回到 1.
// 3. **它如果在更高层看到当前插入的节点,那么它肯定可以在更低层看见当前插入的节点**。
// 4. 如果它每一层都没看见的话,那么这个 reader 在 CPU 中执行时至少一次 insert 修改指针都没有发生,那么它就不应该看见 insert 的值
max_height_.store(height, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
x = NewNode(key, height);
// 注意不能反过来从最高层往下迭代
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
// x 看到的是最新的 prev(FindGreaterOrEqual 中用的是 acquire 内存序的 Next),并且没有其他的 reader 能看见还没插入进去的 x,所以这里对 x 的修改可以不设置 barrier
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
// 但这里就必须设置 Release 的内存序了,reader 会看见 prev[i],按照 for 循环的次序,reader 不会看见 k 层的 x 当却看不到 k - 1 层的 x(Release 保证写入 k - 1 层时会阻止后面的写入先被观察到)
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Contains(const Key& key) const {
// 找后继或者 key 相等的节点,并比较 key
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, nullptr);
// 为什么不写 return x != nullptr && Equal(key, x->key) 呢?所以 google 员工对代码也没那么挑剔,语义一样怎么写都行
if (x != nullptr && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
并发测试
这个 skip list 可以让允许多个读和一个写入并发,所以比较好奇它是怎么测试的
- 测试思路:
// We want to make sure that with a single writer and multiple
// concurrent readers (with no synchronization other than when a
// reader's iterator is created), the reader always observes all the
// data that was present in the skip list when the iterator was
// constructed. Because insertions are happening concurrently, we may
// also observe new values that were inserted since the iterator was
// constructed, but we should never miss any values that were present
// at iterator construction time.
//
// We generate multi-part keys:
// <key,gen,hash>
// where:
// key is in range [0..K-1]
// gen is a generation number for key
// hash is hash(key,gen)
//
// The insertion code picks a random key, sets gen to be 1 + the last
// generation number inserted for that key, and sets hash to Hash(key,gen).
//
// At the beginning of a read, we snapshot the last inserted
// generation number for each key. We then iterate, including random
// calls to Next() and Seek(). For every key we encounter, we
// check that it is either expected given the initial snapshot or has
// been concurrently added since the iterator started.
// 当测试一个写入和多个读取并发时,先创建一个 iterator,这个 reader 应当看见
// 创建时所有的节点,并且它可能会看见目前插入的节点和已经插入的节点。
// 操作的数据:
// We generate multi-part keys:
// <key,gen,hash>
// where:
// key is in range [0..K-1]
// gen is a generation number for key
// hash is hash(key,gen)
// 开始时,read 保存一下当前每个 key 最新的 gen,迭代器执行随机的 Next()
// 和 Seek(),同时会有一个 writer 随机选一个 key,并修改它的 gen 和 hash,
// 迭代器必须保证对于每个 key,它的状态是 initial snapshot 还是 concurrently added.
- 测试过程
测试结构:
typedef uint64_t Key;
class ConcurrentTest {
private:
// K 一共为 4,每个 key 都有 2^32 个 gen
static constexpr uint32_t K = 4;
// Key 按照 key, gen, hash 顺序排序
static uint64_t key(Key key) { return (key >> 40); } // 高3B(0,1,2)作为 key
static uint64_t gen(Key key) { return (key >> 8) & 0xffffffffu; } // 中间4B(3,4,5,6)作为 gen
static uint64_t hash(Key key) { return key & 0xff; } // 低1B(7)作为 hash
static uint64_t HashNumbers(uint64_t k, uint64_t g) {
uint64_t data[2] = {k, g};
return Hash(reinterpret_cast<char*>(data), sizeof(data), 0);
}
static Key MakeKey(uint64_t k, uint64_t g) {
static_assert(sizeof(Key) == sizeof(uint64_t), "");
assert(k <= K); // We sometimes pass K to seek to the end of the skiplist
assert(g <= 0xffffffffu); // 确保 g 的高四B全是0,这样 g << 8 高3B全是0
// 按照上面的格式,拼成 key,高3B为k,中间4B为 g,低1B为hash
return ((k << 40) | (g << 8) | (HashNumbers(k, g) & 0xff));
}
static bool IsValidKey(Key k) {
// 看看 Key 中的 hash 是不是匹配根据 k 和 g 计算出来的 hash
return hash(k) == (HashNumbers(key(k), gen(k)) & 0xff);
}
static Key RandomTarget(Random* rnd) {
switch (rnd->Next() % 10) {
case 0:
// Seek to beginning
return MakeKey(0, 0);
case 1:
// Seek to end,最大的 k 为 K - 1,所以 K 开头的没有后继,是最后一个节点
return MakeKey(K, 0);
default:
// Seek to middle
return MakeKey(rnd->Next() % K, 0);
}
}
// Per-key generation
struct State {
std::atomic<int> generation[K];
void Set(int k, int v) {
// release 写入
generation[k].store(v, std::memory_order_release);
}
// acquire 读出
int Get(int k) { return generation[k].load(std::memory_order_acquire); }
State() {
// 所有 k 的 g 初始化为 0
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++) {
Set(k, 0);
}
}
};
// Current state of the test
State current_;
Arena arena_;
// SkipList is not protected by mu_. We just use a single writer
// thread to modify it.
// 没有 mutex 保护,因为确保只会有一个 writer
SkipList<Key, Comparator> list_;
public:
ConcurrentTest() : list_(Comparator(), &arena_) {}
// REQUIRES: External synchronization
// 这个方法本身需要一个锁保护
void WriteStep(Random* rnd) {
const uint32_t k = rnd->Next() % K; // 随机一个选个 k
const intptr_t g = current_.Get(k) + 1; // 取出它的 g,并 +1,这里的 g 总是大于 0
const Key key = MakeKey(k, g); // 算出新的 key
list_.Insert(key); // 插入进去
current_.Set(k, g); // 更新这个 k 的 g
}
void ReadStep(Random* rnd) {
// Remember the initial committed state of the skiplist.
// 保存创建迭代器前的状态,这个状态需要在之后依旧有效
State initial_state; // 暂且认为是一个 int initial_state[4] 的数组,一共4个key
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++) {
initial_state.Set(k, current_.Get(k)); // 获取每个 key 最新的 gen
}
Key pos = RandomTarget(rnd); // 随机跳到一个地方,这个地方可能在 skip list 里找不到
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Iterator iter(&list_);
iter.Seek(pos); // iter 的 cursor 目前指向 pos 或者 pos 的直接后继,中间可能有 gap
while (true) {
Key current;
if (!iter.Valid()) {
// 如果当前位置没有 key,说明 pos 不存在于 skip list 且没有后继,那么就从 pos 开始到末尾
current = MakeKey(K, 0);
} else {
current = iter.key(); // 取当前位置的 key
// 确保当前的 key 是合法的
ASSERT_TRUE(IsValidKey(current)) << current;
}
// current 会一直往前走
ASSERT_LE(pos, current) << "should not go backwards";
// Verify that everything in [pos,current) was not present in
// initial_state.
// pos 到 current 之间可能有一段距离,且这段距离里的并发插入的 key 在 iter.Seek(pos)
// 之前一定不在 skip list 里(Seek 之后可能有 writer 并发执行而存在,但这里只看 initial_state)
// 那么我们在 iter.Seek(pos) 之前观察到的 initial_state 里一定没有观察到这段 key 的 gen。
// 所以这里检查 initial_state 里的 4 个 key 的 gen 是否总是小于这段 gap 里的可能
// 插入的 key 的 gen。
while (pos < current) {
ASSERT_LT(key(pos), K) << pos;
// Note that generation 0 is never inserted, so it is ok if
// <*,0,*> is missing.
// 由于 gen = 0 不会被插入(current_.Get(k) + 1 总是 > 0),所以不用检查 gen = 0 的 key
ASSERT_TRUE((gen(pos) == 0) ||
(gen(pos) > static_cast<Key>(initial_state.Get(key(pos)))))
<< "key: " << key(pos) << "; gen: " << gen(pos)
<< "; initgen: " << initial_state.Get(key(pos));
// Advance to next key in the valid key space
if (key(pos) < key(current)) {
// 跳过一整个 key space,去检查 initial_state 里下一个 key
pos = MakeKey(key(pos) + 1, 0);
} else {
// current > pos,所以这里 key(pos) = key(current),往后移动一个 gen,
// 直到遇到 current
pos = MakeKey(key(pos), gen(pos) + 1);
}
}
// 直到迭代到末尾
if (!iter.Valid()) {
break;
}
// 迭代器往后推进一个随机的距离
if (rnd->Next() % 2) {
iter.Next();
pos = MakeKey(key(pos), gen(pos) + 1); // 最后一个 pos 已经检查过了(current),跳过
} else {
Key new_target = RandomTarget(rnd);
if (new_target > pos) {
pos = new_target;
iter.Seek(new_target);
}
}
}
}
};
测试样例:
// Simple test that does single-threaded testing of the ConcurrentTest
// scaffolding.
// 单线程测试(确保原子指令不会重排)
TEST(SkipTest, ConcurrentWithoutThreads) {
ConcurrentTest test;
Random rnd(test::RandomSeed());
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
test.ReadStep(&rnd);
test.WriteStep(&rnd);
}
}
// 多线程测试
class TestState {
public:
ConcurrentTest t_;
int seed_;
std::atomic<bool> quit_flag_;
// 三个状态,以及同步用途的 Wait 和 Change
enum ReaderState { STARTING, RUNNING, DONE };
explicit TestState(int s)
: seed_(s), quit_flag_(false), state_(STARTING), state_cv_(&mu_) {}
void Wait(ReaderState s) LOCKS_EXCLUDED(mu_) {
mu_.Lock();
while (state_ != s) {
state_cv_.Wait();
}
mu_.Unlock();
}
void Change(ReaderState s) LOCKS_EXCLUDED(mu_) {
mu_.Lock();
state_ = s;
state_cv_.Signal();
mu_.Unlock();
}
private:
port::Mutex mu_;
ReaderState state_ GUARDED_BY(mu_);
port::CondVar state_cv_ GUARDED_BY(mu_);
};
// 并发读
static void ConcurrentReader(void* arg) {
TestState* state = reinterpret_cast<TestState*>(arg);
Random rnd(state->seed_);
int64_t reads = 0;
state->Change(TestState::RUNNING);
while (!state->quit_flag_.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) {
state->t_.ReadStep(&rnd);
++reads;
}
state->Change(TestState::DONE);
}
static void RunConcurrent(int run) {
// run 就只拿来设置个种子?
const int seed = test::RandomSeed() + (run * 100);
Random rnd(seed);
const int N = 1000;
const int kSize = 1000;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// 一次测试一个读和一个写并发
if ((i % 100) == 0) {
// 进度汇报
std::fprintf(stderr, "Run %d of %d\n", i, N);
}
TestState state(seed + 1);
// 只有一个读
Env::Default()->Schedule(ConcurrentReader, &state);
// 等待这个读 task 被调度
state.Wait(TestState::RUNNING);
// 只有一个写
for (int i = 0; i < kSize; i++) {
state.t_.WriteStep(&rnd);
}
// 写完后退出
state.quit_flag_.store(true, std::memory_order_release);
// 等待这个读结束
state.Wait(TestState::DONE);
}
}
TEST(SkipTest, Concurrent1) { RunConcurrent(1); }
TEST(SkipTest, Concurrent2) { RunConcurrent(2); }
TEST(SkipTest, Concurrent3) { RunConcurrent(3); }
TEST(SkipTest, Concurrent4) { RunConcurrent(4); }
TEST(SkipTest, Concurrent5) { RunConcurrent(5); }
总结
总的来说,这是一个很不错的实现,简单的同时还具备一些无锁并发的能力。
最后的并发测试部分有一些迷惑,并没有看见多个读和一个写入并发的测试。